Planetary system
"Solar systems" redirects here. For the planetary system of the Sun, see
Solar System. For the solar power company, see Solar Systems (company).

An artist's concept of a planetary system
A planetary system consists of the various non-stellar objects orbiting a star such as planets, dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, meteoroids, comets, and cosmic dust.[1][2] The Sun together with its planetary system, which includes Earth, is known as the Solar System.[3][4]
Origin and evolution
Planetary systems are generally believed to form as part of the same process which results in star formation. Some early theories involved another star passing extremely close to the Sun, drawing material out from it which then coalesced to form the planets. However, the probability of such a near collision is now known to be far too low to make this a viable model. Accepted theories today argue that a protoplanetary disk forms by gravitational collapse of a molecular cloud and then evolves into a planetary system by collisions and gravitational capture.[5]
Some planetary systems may form differently, however. Planets orbiting pulsars—stars which emit periodic bursts of electromagnetic radiation—have been discovered by the slight variations they cause in the timing of these bursts. Pulsars are formed in violent supernova explosions, and a normal planetary system could not possibly survive such a blast—planets would either evaporate, be pushed off of their orbits by the masses of gas from the exploding star, or the sudden loss of most of the mass of the central star would see them escape the gravitational hold of the star. One theory is that existing stellar companions were almost entirely evaporated by the supernova blast, leaving behind planet-sized bodies. Alternatively, planets may somehow form in the accretion disk surrounding pulsars.[6]
List of planetary systems

Artist's concept of a distant planetary system
- Solar System – the Sun and its planetary system, the first such system discovered
- PSR B1257+12 – the first extrasolar planetary system discovered, the first pulsar planetary system discovered, the first multi exoplanet system discovered
- Upsilon Andromedae – the first multiplanet extrasolar planetary system discovered around a main sequence star, found to be so in April 1999
- PSR B1620-26 – the first multistar planetary system discovered.
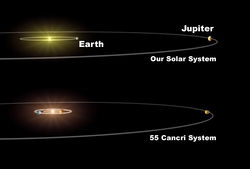
- 55 Cancri – the largest known extrasolar planetary system prior to the discovery of the HD 10180 system (5 known planets as of November 6, 2007, along with a distant stellar companion.)[7]
- Gliese 876 – the first system around a red dwarf star and the first discovered to have an orbital resonance (subsequently shown to be a 3-body Laplace resonance).[8][9]
- HD 69830 – found to have three Neptune-mass planets and an asteroid belt, all within 1 AU[10][11]
- 2M1207 – the first imaged system and the first brown dwarf system with a planet discovered[12]
- Gliese 581 - first extrasolar system discovered with a super-Earth planet located within the habitable zone (Gliese 581 d)[13]
- Mu Arae - the system's innermost planet was the first "hot Neptune" to be discovered
- 16 Cygni - the first triple star planetary system discovered
- HD 37124
- HD 12661
- HD 73526
- 47 Ursae Majoris
- Epsilon Eridani
- 14 Herculis
- UX Tau A
- HD 10180 – system with 5 confirmed and 2 currently unconfirmed planets, being the largest known extrasolar planetary system.[14]
- Kepler-9 - the first pair of transiting exoplanets found to be in a mean motion resonance
See also
References
- ↑ p. 394, The Universal Book of Astronomy, from the Andromeda Galaxy to the Zone of Avoidance, David J. Dsrling, Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley, 2004. ISBN 0471265691.
- ↑ p. 314, Collins Dictionary of Astronomy, Valerie Illingworth, London: Collins, 2000. ISBN 0-00-710297-6.
- ↑ p. 382, Collins Dictionary of Astronomy.
- ↑ p. 420, A Dictionary of Astronomy, Ian Ridpath, Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press, 2003. ISBN 0-19-860513-7.
- ↑ planetary systems, formation of, David Darling, entry in The Internet Encyclopedia of Science, accessed on line September 23, 2007.
- ↑ Planet formation scenarios, Philipp Podsiadlowski, pp. 149–165, in Planets around pulsars; Proceedings of the Conference, California Inst. of Technology, Pasadena, Apr. 30-May 1, 1992, edited by J. A. Phillips, J. E. Thorsest, and S. R. Kulkarni, ASP Conference Series, 36, 1993.
- ↑ Wired News (2002-06-13). "Found: Solar System Like Our Own". http://www.wired.com/news/technology/0,1282,53188,00.html.
- ↑ Marcy, Geoffrey W.; Butler, R. Paul; Fischer, Debra; Vogt, Steven S.; Lissauer, Jack J.; Rivera, Eugenio J. (2001). "A Pair of Resonant Planets Orbiting GJ 876". The Astrophysical Journal 556 (1): 296–301. doi:10.1086/321552.
- ↑ Rivera, Eugenio J.; Laughlin, Gregory; Butler, R. Paul; Vogt, Steven S.; Haghighipour, Nader; Meschiari, Stefano (June 2010). "The Lick-Carnegie Exoplanet Survey: A Uranus-mass Fourth Planet for GJ 876 in an Extrasolar Laplace Configuration". arΧiv:1006.4244v1 [astro-ph.EP].
- ↑ Whitney Clavin (2005-04-20). "NASA's Spitzer Telescope Sees Signs of Alien Asteroid Belt". http://www.spitzer.caltech.edu/Media/releases/ssc2005-10/release.shtml.
- ↑ Christophe Lovis; Michel Mayor (2006-05-18). Trio of Neptunes and their Belt. http://www.eso.org/outreach/press-rel/pr-2006/pr-18-06.html.
- ↑ Robert Roy Britt (2004-09-10). "Likely First Photo of Planet Beyond the Solar System". http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/planet_photo_040910.html.
- ↑ "Lightest exoplanet yet discovered". eso.org. 2009-04-21. http://www.eso.org/public/outreach/press-rel/pr-2009/pr-15-09.html. Retrieved 2009-04-27.
- ↑ http://exoplanet.eu/star.php?st=HD+10180
|
Exoplanets |
|
|
|
|
| Classes |
Carbon planet • Chthonian planet • Circumbinary planet • Coreless planet • Eccentric Jupiter • Goldilocks planet • Helium planet • Hot Jupiter • Hot Neptune • Iron planet • Jovian planet • Ocean planet • Puffy planet • Pulsar planet • Super-Earth • Terrestrial planet |
|
| Systems |
Binary star • Extragalactic planet • Extrasolar moon • Hypothetical extrasolar planet • Planetary system • Rogue planet • Trojan planet
|
|
| Lists |
Stars with extrasolar planets • Extrasolar planet extremes • Extrasolar planet firsts • Unconfirmed exoplanets
|
|
| Surveys |
|
Exoplanets search projects |
|
| Ground-based |
AAPS • California and Carnegie Planet Search • HAT • HARPS, part of the Geneva Extrasolar Planet Search • MEarth Project • MOA • OGLE • Magellan Planet Search Program • SuperWASP • TrES • XO Telescope • EAPSNet • High Resolution Echelle Spectrometer (HIRES) • MARVELS • MUSCA • Microlensing Follow-Up Network (MicroFUN) • NASA-UC Eta-Earth • PHASES • PlanetPol • PARAS • Subaru telescope, using the High-Contrast Coronographic Imager for Adaptive Optics (HiCIAO) • Systemic, an amateur search project • ZIMPOL/CHEOPS, based at the VLT
|
|
| Space Missions |
|
Current
|
EPOXI (2005) • SWEEPS (2006) • COROT (2006) • Kepler (2009) |
|
|
Planned
|
PEGASE (est. 2010-2012) • TESS (est. 2012-2013) • New Worlds (est. 2014) • SIMS (est. 2015-2016) • PLATO (est. 2017)
|
|
|
Other status
|
TPF (deferred) • Darwin (deferred) • Eddington (cancelled)
|
|
|
|
| See also: Discoveries of extrasolar planets |
|
|
Star |
|
| Evolution |
|
|
| Protostars |
|
|
| Luminosity class |
|
|
| Spectral classification |
O · B · A · F · G · K · Be · OB · Subdwarf B · Late-type · Peculiar (Am · Ap/Bp (Oscillating) · Barium · Carbon · CH · Extreme helium · Lambda Boötis · Mercury-manganese · S · (Technetium) · Shell · Lead
|
|
| Remnants |
|
|
Failed and
theoretical stars |
Substellar object (Brown dwarf · Sub-brown dwarf · Planetar) · Boson star · Dark-matter star · Quasistar · Thorne–Żytkow object · Iron star
|
|
| Nucleosynthesis |
|
|
| Structure |
Core · Convection zone (Microturbulence · Oscillations) · Radiation zone · Photosphere · Starspot · Chromosphere · Corona · Stellar wind (Bubble) · Asteroseismology · Eddington luminosity · Kelvin–Helmholtz mechanism
|
|
| Properties |
|
|
| Star systems |
|
|
Earth-centric
observation of |
|
|
| Lists |
Star names · Most massive · Least massive · Largest · Brightest (Historical) · Most luminous · Nearest (Nearest bright) · Brown dwarfs · Planetary nebulae · Novae · Notable supernovae · Supernova remnants · Supernova candidates · Timeline of stellar astronomy
|
|
| Related articles |
|
|
 Star portal Star portal |
|